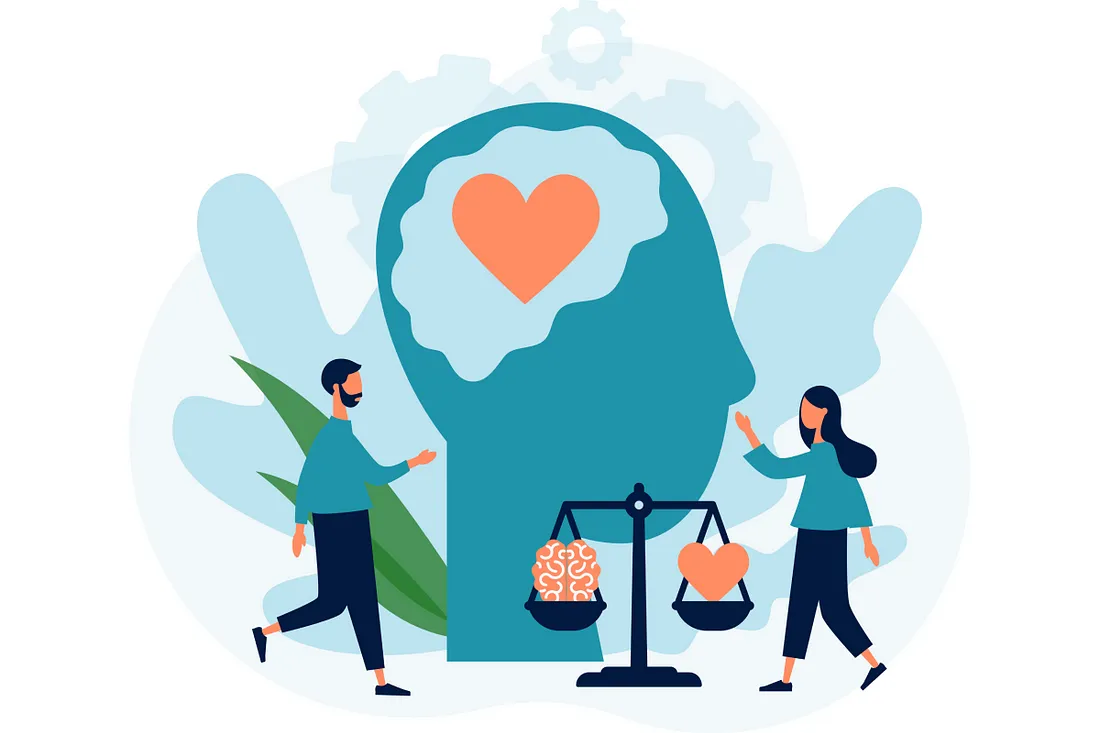
Emotional intelligence, often called EI or EQ (emotional quotient), encompasses the capacity to perceive, interpret, display, regulate, appraise, and employ emotions as a means of effective and constructive communication and interpersonal engagement. Proficiency in expressing and managing emotions is undoubtedly crucial, yet equally vital is the competence in comprehending, deciphering, and responding to the emotional experiences of others. Specific experts posit that emotional intelligence carries more significance than IQ in achieving success in various facets of life.
Indications of Emotional Intelligence
Several key manifestations and instances of emotional intelligence encompass:
- Discerning and articulating others’ emotional states
- Cognizance of personal strengths and limitations
- Self-assuredness and self-acknowledgment
- The aptitude to relinquish past errors
- An inclination to adapt to and embrace change
- A robust inquisitiveness, especially regarding individuals
- Experiencing empathy and demonstrating concern for others
- Demonstrating responsiveness to others’ sentiments
- Assuming accountability for one’s own mistakes
- Proficiency in managing emotions during challenging circumstances
Assessment of Emotional Intelligence
Numerous assessment tools have emerged to gauge levels of emotional intelligence, generally falling into two primary categories: self-report assessments and ability assessments.
Self-report assessments are the most prevalent due to their ease of administration and scoring. Respondents provide their evaluations in response to questions or statements. For instance, when presented with a message like “I frequently believe that I grasp others’ emotional states,” an individual might select from options such as disagree, somewhat disagree, agree, or strongly agree.
Conversely, ability assessments entail individuals responding to various scenarios that evaluate their aptitudes. These tests often necessitate practical skills demonstrations, which an impartial third party subsequently considers.
What Are the Four Elements of Emotional Intelligence?
Scholars categorize emotional intelligence into four distinct elements: emotional perception, reasoning through emotions, comprehension of emotions, and emotional management.
- Emotional Perception: The initial stride in comprehending emotions involves accurate perception. This often entails deciphering nonverbal cues, such as body language and facial expressions.
- Reasoning with Emotions: Subsequently, emotions are harnessed to facilitate thinking and cognitive processes. Emotions play a role in prioritizing our focus and reactions, directing our emotional responses towards stimuli that command our attention.
- Emotion Comprehension: The array of emotions we perceive carries many connotations. When confronted with someone’s display of anger, the observer must construe the underlying triggers and potential implications. For instance, if a supervisor exhibits signs of irritation, it could indicate dissatisfaction with work, frustration from receiving a traffic ticket that morning, or conflicts in personal relationships.
- Emotional Management: Proficiency in handling emotions is a pinnacle of emotional intelligence. Skillfully regulating one’s own emotions, as well as aptly addressing the feelings of others, constitute pivotal aspects of dynamic governance.
This model delineates the four facets hierarchically, ascending in complexity. The rudimentary processes reside in the lower tiers, encompassing emotional perception and expression, while the upper echelons necessitate heightened conscious engagement and encompass emotional regulation.
Impact of Emotional Intelligence
Interest in fostering social and emotional intelligence within educational contexts has recently surged. Social and emotional learning (SEL) initiatives have integrated themselves as integral components of numerous school curricula.
The overarching objective of these endeavors transcends mere enhancement of well-being; it extends to academic advancement and the prevention of bullying. Instances abound, exemplifying the pervasive role emotional intelligence assumes in everyday existence.
Cautious Deliberation
Individuals endowed with emotional intelligence recognize the potent yet transient nature of emotions. Confronted with emotionally charged situations, such as harboring frustration toward a colleague, a response characterized by emotional intelligence would entail allowing a pause before reacting. This interval facilitates dynamic equilibrium and fosters more judicious contemplation of all facets entwined within the disagreement.
Elevated Self-Insight
Emotionally intelligent individuals excel not only in contemplating the emotional states of others but also in comprehending their sentiments. Self-awareness empowers individuals to embrace the intricate interplay of diverse factors influencing their emotional experiences.
Empathic Engagement
Substantial portions of emotional intelligence encompass the capacity to contemplate and empathize with others’ emotional landscapes. This often necessitates envisioning one’s response under analogous circumstances, a mental exercise in understanding shared sentiment.
Utilizing Emotional Intelligence in Practical Situations
The application of emotional intelligence in your day-to-day life offers a multitude of avenues. Several ways to implement and cultivate emotional intelligence encompass:
• Embracing constructive criticism and taking accountability
• Navigating onward after making errors
• Asserting your right to decline when necessary
• Engaging in open sharing of emotions with others
• Devising solutions to challenges that cater to all involved parties
• Harboring empathy toward fellow individuals
• Cultivating exceptional listening aptitude
• Unraveling the motives behind your actions
• Abstaining from passing judgement on others
The role of emotional intelligence in nurturing effective interpersonal exchanges cannot be overstated. Some authorities even assert that this prowess significantly determines life achievements more than IQ alone. Thankfully, there are methods to augment your own social and emotional intelligence.
The Significance of Emotional Intelligence
Grasping emotions is the linchpin to fostering improved relationships, heightened well-being, and fortified communication proficiencies.
Potential Drawbacks of Emotional Intelligence
Diminished emotional intelligence skills can precipitate potential pitfalls that reverberate across domains, encompassing work and relationships. Individuals with limited emotional acumen tend to engage in more disputes, maintain relationships of lower quality, and exhibit inadequate emotional coping mechanisms.
However, possessing an exceedingly elevated emotional skill level also presents challenges. For instance:
• Evidence proposes that individuals with markedly high emotional intelligence might experience curbed creativity and innovation.
• Excessively emotionally intelligent individuals might find themselves grappling with delivering negative feedback, fearing its impact on others’ sentiments.
• Research has unearthed instances where heightened EQ could be employed for manipulative and deceitful motives.
Enhancing Emotional Intelligence: Strategies for Growth
While innate emotional aptitudes vary among individuals, emerging evidence suggests that the refinement and augmentation of emotional skills are attainable through deliberate cultivation. A noteworthy instance is a 2019 randomized controlled trial that established the potential of vigorous intelligence training to enhance emotional competencies in professional environments.
Acknowledging the Significance of Emotional Intelligence
Recognising the importance of emotional intelligence prompts the quest for steps to nurture one’s own social and emotional proficiencies. Presented below are valuable insights and methods to embark upon this enhancement journey.
Attentive Listening
Comprehending others’ emotional states commences with attentive listening. Devote time and attention to absorb both verbal and non-verbal cues. Non-verbal signals, such as body language, often convey substantial meaning. When detecting specific emotional undertones, investigate the multifaceted factors influencing the observed sentiment.
Empathetic Engagement
Beyond perceiving emotions lies the art of empathy — stepping into someone else’s shoes to genuinely grasp their perspective. Hone empathic abilities through deliberate practice. Envision yourself within their circumstances and contemplate their emotional responses. Such exercises foster an immediate understanding of particular situations and the long-term development of robust emotional skills.
Contemplative Analysis
Critical to emotional intelligence is the skill to reason through emotions. Reflect on the influence of your feelings on choices and behaviors. When assessing others’ reactions, delve into the interplay of their emotional states.
Pose Inquiries: Why is this individual experiencing these emotions? Might concealed factors contribute to their emotional state? How do your feelings diverge from theirs? Exploring such inquiries can illuminate the role of emotions in shaping thoughts and conduct.
Engaging in a deliberate process of enhancing emotional intelligence contributes to a more profound comprehension of oneself and others, bolstering effective interpersonal connections and enriching emotional understanding.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving tapestry of human interactions, cultivating emotional intelligence is a beacon of personal and social growth. As we navigate the intricate terrain of emotions, these strategies to enhance emotional intelligence provide a compass, guiding us toward more profound understanding, heightened empathy, and effective communication. As skilled artisan refines their craft over time, so can we refine our ability to perceive, interpret, and harness emotions, creating a harmonious symphony of connections that enrich our lives and those around us. Through diligent practice and introspection, nurturing emotional intelligence becomes an empowering voyage towards greater self-awareness and profound human connection.