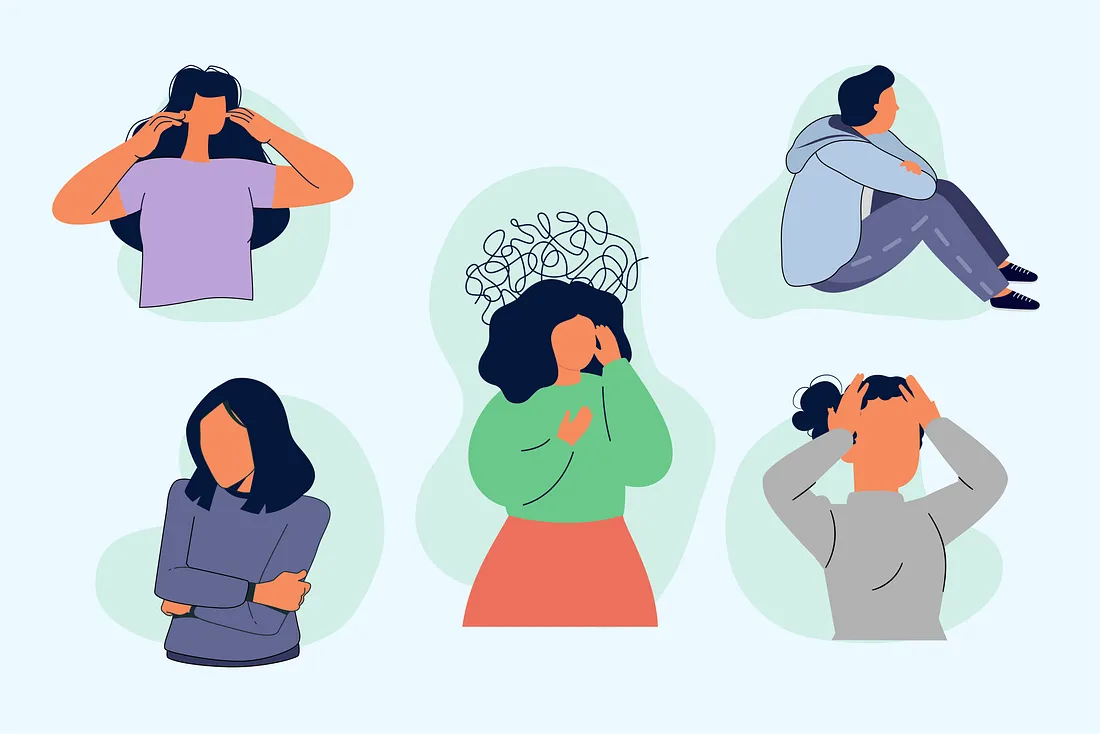
Anxiety is a category of mental health disorders that are identified by excessive worry, fear, and nervousness. These disorders can cause immense distress, impair functioning, and affect the quality of life. This article explores the different types of anxiety disorders, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options. You can recognize the signs and seek appropriate help by better understanding these conditions.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is a common anxiety disorder that affects approximately 6.8 million adults in the United States. It is characterized by excessive, persistent, and uncontrollable worry about everyday concerns like work, finances, health, and relationships. People with GAD experience extreme anxiety and tension even without apparent reason. This anxiety can cause physical symptoms such as muscle tension, fatigue, headaches, and difficulty sleeping.
Symptoms of GAD can vary from person to person, but some common signs include the following:
- Persistent and excessive worry
- Inability to control worry
- Restlessness and irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Muscle tension
- Fatigue
- Sleep disturbances
The causes of GAD are not fully understood, but research suggests that a combination of biological, genetic, and environmental factors may contribute to its development. Treatment options for GAD include psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes such as exercise, meditation, and stress-management techniques. People with GAD can learn to manage their anxiety and lead fulfilling lives with proper treatment and support.
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by unexpected and recurring panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden and intense episodes of fear or discomfort that peak within minutes and are accompanied by physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, sweating, trembling, and shortness of breath. Panic attacks can occur unexpectedly or be triggered by specific situations or activities, such as public speaking or driving on the highway.
Symptoms of panic disorder include:
- Recurrent panic attacks
- Persistent worry about having future panic attacks
- Fear of losing control or dying
- Avoidance of places or situations that may trigger panic attacks
Although the precise reasons for panic disorder are uncertain, it is thought that a combination of genetic, biological, and environmental factors may contribute to its development. Treatment options for panic disorder include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), medication, and relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation. People with panic disorder can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life with proper treatment and support.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder, also known as social phobia, is characterized by an intense and persistent fear of social situations or performances. People with social anxiety disorder experience excessive anxiety and self-consciousness in social situations and may avoid them altogether. This fear can cause physical symptoms such as sweating, blushing, shaking, and nausea.
Symptoms of a social anxiety disorder include:
- Fear of social situations or performances
- Excessive worry about embarrassing oneself in social situations
- Avoidance of social situations
- Physical symptoms such as sweating, blushing and trembling
The exact causes of social anxiety disorder are unknown, but researchers believe genetic, biological, and environmental factors may contribute to its development. Treatment options for social anxiety disorder include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, medication, and relaxation techniques. Individuals who suffer from social anxiety disorder can enhance their quality of life and cope with symptoms effectively with appropriate support and treatment.
Specific Phobias
Specific phobias are a type of anxiety disorder characterized by an intense and irrational fear of a particular object, situation, or activity. The fear is excessive and disproportionate to the actual danger the object or situation poses. As a result, people with specific phobias may avoid the feared object or condition, which can severely limit their daily activities and quality of life.
Manifestations of specific phobias consist of the following:
- Extreme terror or unease when encountering the dreaded object or situation
- Evading the feared object or situation
- Physiological reactions, such as sweating, shaking, and rapid heartbeat.
Specific phobias can develop in childhood or adulthood and can be caused by genetic, biological, or environmental factors. Treatment options for specific phobias include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and medication. People with specific phobias can overcome their fear and improve their quality of life with proper treatment and support.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is described as an anxiety disorder where individuals experience recurring thoughts, images, or impulses (obsessions) and engage in repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) in an effort to alleviate anxiety or avert potential harm. Even though individuals with OCD may acknowledge that their thoughts or behaviors are illogical, they still feel an urge to carry them out.
Symptoms of OCD include:
- Obsessions, such as fear of contamination, harm, or intrusive thoughts
- Compulsions, such as excessive cleaning, checking, or counting
- Distress and anxiety caused by obsessions and compulsions
- Time-consuming rituals that interfere with daily life
The causes of OCD are not fully understood, but research suggests that genetic, biological, and environmental factors may contribute to its development. Treatment options for OCD include:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT).
- Exposure and response prevention therapy.
- Medication like Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs).
Individuals who have OCD can enhance their quality of life and cope with their symptoms effectively through adequate treatment and support.
Conclusion
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions that can cause significant distress and impair daily functioning. Generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, specific phobias, and obsessive-compulsive disorder are the most common types of anxiety disorders. These conditions can be caused by genetic, biological, and environmental factors and can be treated with medication, psychotherapy, or a combination. If you suspect that you might be suffering from an anxiety disorder, it is crucial to obtain expert assistance from a physician or a mental health specialist.
People with anxiety disorders can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life with proper treatment and support.
EaseCare Links
Website | Facebook | Instagram | Get help | Free Mental Health Assessment