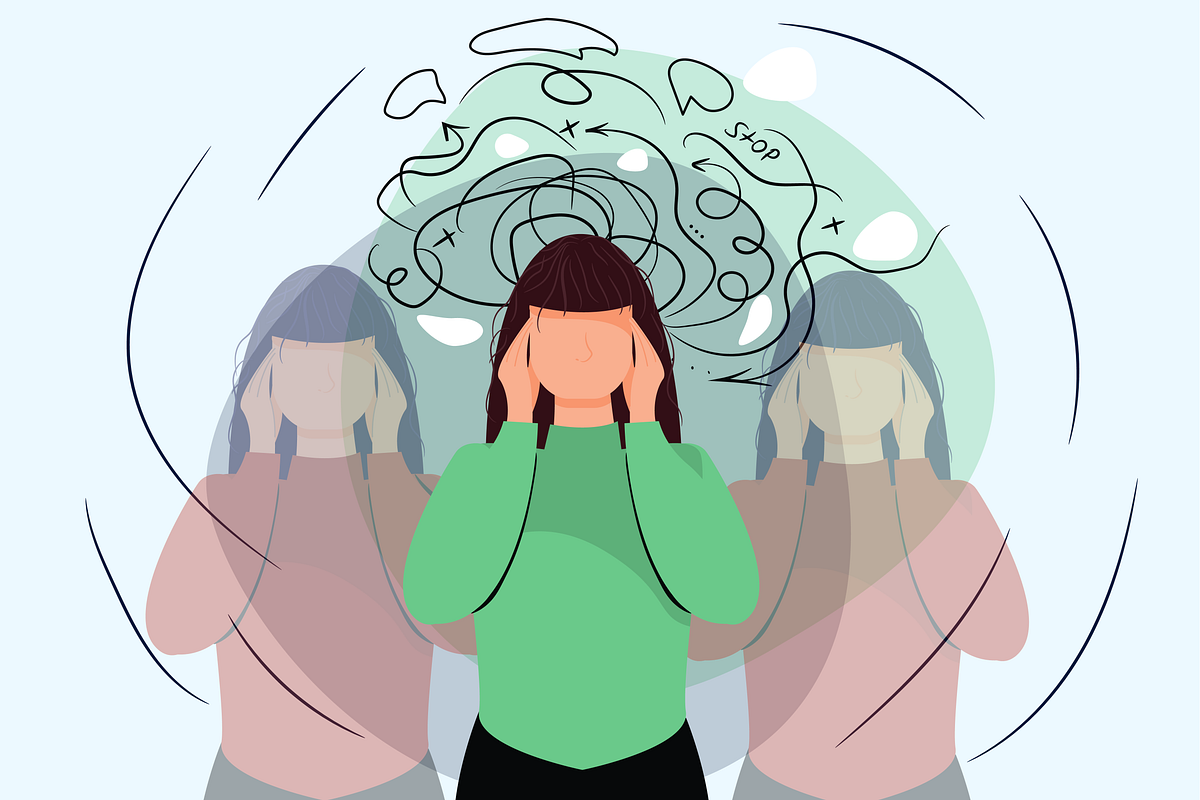
Experiencing anxiety is a normal aspect of human existence. It’s not unusual to feel apprehensive, sense a fluttering in your gut, or struggle to cease ruminating on a specific matter. Nonetheless, if anxiety is a recurring issue for you, it’s natural to question if it constitutes a mental health disorder. In this article, we will delve into the concept of mental illness, the situations where anxiety could indicate a mental health problem, and the methods for identifying and addressing anxiety-related disorders.
Defining Mental Illness:
Mental illnesses are psychiatric conditions that affect an individual’s mood, behavior, and thoughts. They are widespread, with about one in five people experiencing mental illness and up to 4% experiencing a severe form. The condition must significantly impact a person’s daily functioning to be considered a mental illness.
Mental illness can be short-term for some, but for many, it is a lifelong condition requiring careful management and effective treatment. In addition, mental illnesses can hinder functionality if left untreated, impacting careers, relationships, and family dynamics. Fortunately, individuals with mental illnesses can lead fulfilling lives with proper treatment.
Common mental illnesses include:
- Depression (unipolar and bipolar)
- Anxiety disorders
- Personality disorders (e.g., borderline and narcissistic)
- Psychotic disorders
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Substance abuse disorder
- Eating disorders
Anxiety as a Mental Illness
Anxiety as an emotion is not a mental illness. Instead, it is a typical human experience that arises in various situations, such as before a presentation, meeting new people, starting a new job, or facing potential danger.
However, anxiety can be indicative of a mental illness in some cases. Anxiety disorders share several common characteristics:
- They can disrupt daily life and hinder functionality
- The fear and anxiousness can be intense, overwhelming, and persistent
- Anxiety disorders often involve perceiving nonexistent threats or exaggerating existing ones.
Approximately 30% of adults will experience an anxiety disorder in their lifetime. Some populations, such as women, those with chronic conditions, and younger individuals, may be more susceptible to anxiety disorders.
Common anxiety disorders include:
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Panic disorder
- Social anxiety disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Phobias
Diagnosing Anxiety
If you are uncertain whether you are experiencing situational anxiety or an anxiety disorder, seek a proper diagnosis. First, start with your primary care physician to rule out any physical health conditions that may share anxiety symptoms, such as thyroid or heart issues.
In the event that an anxiety disorder is suspected by your physician, they will typically recommend that you undergo additional evaluation by a licensed therapist or psychiatrist.
To determine mental health diagnoses, therapists engage in discussions with their patients about their symptoms and personal experiences. They utilize the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) to diagnose particular anxiety disorders based on the patient’s disclosed information.
Treating Anxiety
Anxiety disorder treatment typically involves a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Therapy
Talk therapy with a qualified counselor or therapist is an effective way to manage anxiety. Your therapist can help identify anxiety triggers and develop coping strategies.
Medication
Medications, such as antidepressants (SSRIs), can help alleviate anxiety symptoms. In addition, for specific instances of anxiety, such as panic attacks, anti-anxiety medication (usually benzodiazepines) may be prescribed. Consult your doctor or psychiatrist to determine the best remedy for your situation.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications can also benefit individuals with anxiety. For example, adequate sleep, relaxation techniques, regular meditation, stress reduction, exercise, and caffeine reduction can all contribute to lessening anxiety symptoms.
Support System
Having a solid support system is crucial for managing anxiety disorders. Friends, family, and support groups can offer a sense of belonging, encouragement, and understanding. Don’t hesitate to reach out to people you trust for help and support during difficult times.
Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief from anxiety symptoms through alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, or herbal supplements. Although these treatments may be helpful, discussing them with your healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific needs is essential.
Conclusion
Anxiety is a natural human emotion that everyone experiences at some point. However, when anxiety becomes overwhelming, persistent, and disrupts daily functioning, it may indicate an anxiety disorder. Proper diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the lives of those living with anxiety disorders. By understanding the connection between anxiety and mental illness, we can work towards reducing stigma and providing better support and care for those affected. Remember, reaching out to your healthcare provider, utilizing therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes, and developing a solid support system are all crucial steps to managing anxiety disorders effectively. Don’t be afraid to seek help and explore various treatments to find the best approach for your unique situation.
EaseCare Links
Website | Facebook | Instagram | Get help | Free Mental Health Assessment